Kali Linux Penetration Testing on Android
Kali Linux is the Most loved Penetration Testing Operating System among the community of Information Security Researchers . Android on the other hand is the most loved Smartphone OS . There have been a lot of discussions in the past about running Kali Linux on Android Platform . In this Tutorial we will be running the Kali Linux OS on the Android Platform and using it for Penetration Testing .
For achieving this we will need to run the Kali OS on the ARM Architecture . This however does not mean you cannot install Kali Linux in a chroot on almost any modern device that runs Android. In fact, the developers of Linux Deploy have made it extremely easy to get any number of Linux distributions installed in a chroot environment using a simple GUI builder.
Prerequisites for Installing Kali Linux on Android using Linux Deploy
- A device running Android 2.1 and above, rooted.
- At least 5 GB free space on internal or external storage.
- A fast, wireless internet connection.
- Patience to wait for a distribution to bootstrap from the network.
Configuring Linux Deploy for Kali
There’s actually very little to be done to get Kali installed. By choosing Kali Linux in the “Distribution” tab, you’ve pretty much covered the important stuff. Optionally, you can choose your architecture, verify that the Kali mirror is correct, set your installation type and location on your Android device, etc. Generally speaking, the defaults provided by Linux Deploy are good to begin with.
Building the Kali Image
Once you are happy with all the settings, hitting the “install” button will start a Kali Linux bootstrap directly from our repositories. Depending on your Internet connection speed, this process could take a while. You’ll be downloading a base install of Kali Linux (with no tools) at minimum.
Start your chrooted Kali
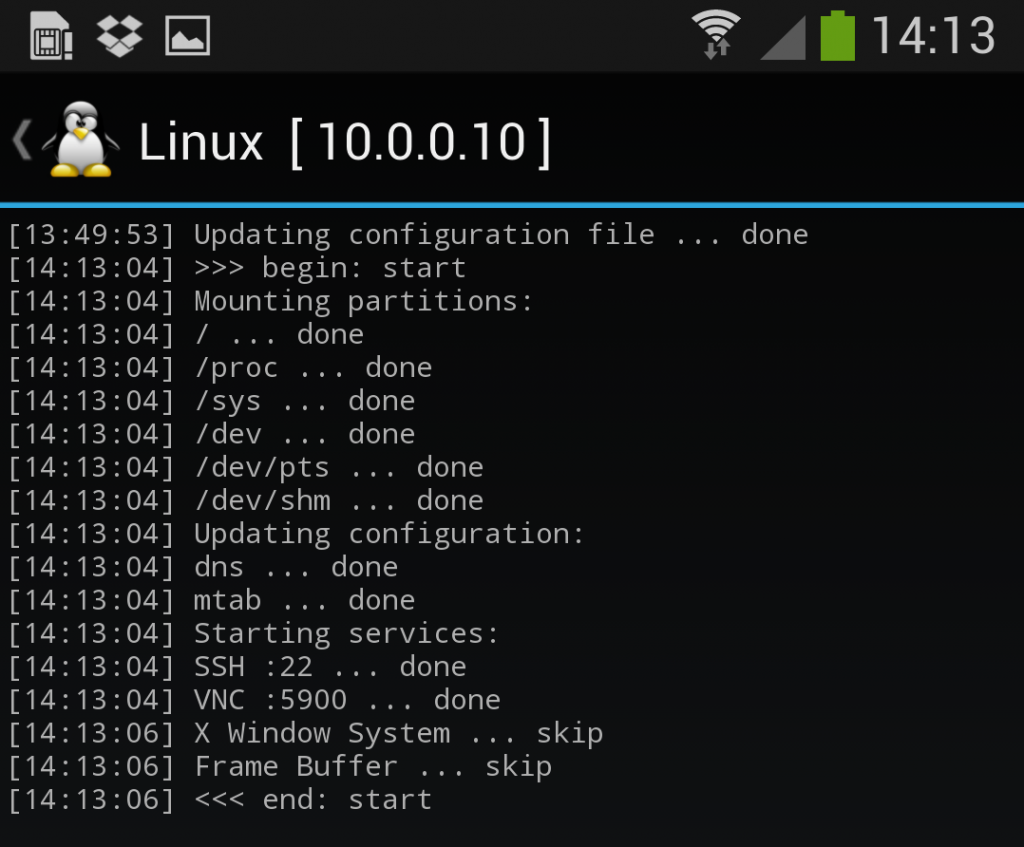
Once the installation is complete, you can have Linux Deploy automatically mount and load up your Kali Linux chroot image. This also includes the starting of services such as SSH and VNC for easier remote access. All of this is automagically done by hitting the “start” button. You should see Linux Deploy setting up your image with output similar to the following:
At this stage, Linux Deploy has started a VNC and SSH server inside your chrooted Kali image. You can connect to the Kali session remotely using the IP address assigned to your Android device (in my case, 10.0.0.10).
Login to your chrooted Kali
The Kali Instance can now be Accessed either through a VNC client or an SSH client to begin the Penetration testing . The VNC password is “changeme” and the SSH credentials are “android” for the username (configured via Linux Deploy) and “changeme” as the password.
muts@slim:~$ ssh android@10.0.0.10 android@10.0.0.10 password: Linux localhost 3.4.5-447845 #1 SMP PREEMPT Fri Apr 12 17:22:34 KST 2013 armv7l Kali GNU/Linux 1.0 [running on Android via Linux Deploy] android@localhost:~$ sudo su root@localhost:/home/android# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/loop3 4180944 667268 3304012 17% / tmpfs 952708 80 952628 1% /dev tmpfs 952708 0 952708 0% /dev/shm root@localhost:/home/android# root@localhost:/home/android# apt-get update Hit http://http.kali.org kali Release.gpg Hit http://http.kali.org kali Release Hit http://http.kali.org kali/main Sources Hit http://http.kali.org kali/contrib Sources Hit http://http.kali.org kali/non-free Sources Hit http://http.kali.org kali/main armel Packages Hit http://http.kali.org kali/contrib armel Packages Hit http://http.kali.org kali/non-free armel Packages Ign http://http.kali.org kali/contrib Translation-en_US Ign http://http.kali.org kali/contrib Translation-en Ign http://http.kali.org kali/main Translation-en_US Ign http://http.kali.org kali/main Translation-en Ign http://http.kali.org kali/non-free Translation-en_US Ign http://http.kali.org kali/non-free Translation-en Reading package lists... Done root@localhost:/home/android#
Image Size Considerations
If left unchanged, Linux Deploy will automatically set an image size of around 4 GB, for a “naked” installation of Kali. If you would like to install additional Kali tools down the road, you might want to consider using a larger image size, which is configurable via the settings in Linux Deploy.

No comments